Development of an ALE formulation for YALES2 — CORIA Internship (YALES2 / SPS)
Delamare Yanis — EP5 SP Engineering Internship
Period: 10 February 2025 – 8 August 2025
>> Visit the internship follow-up & documentation website (access restricted) <<


Overview
This internship was carried out at the CORIA laboratory (UMR 6614 CNRS) and focused on the development and validation of an Arbitrary Lagrangian–Eulerian (ALE) formulation for the diphasic solver SPS within the YALES2 platform. The objective was to provide a robust, maintainable ALE-capable implementation compatible with unstructured and dynamically adaptive meshes, enabling accurate simulation of two-phase flows with mesh motion and refinement.
Work performed included code refactoring, ALE scheme implementation, mesh motion management, and validation on several test cases (droplet, falling cylinder). The project also produced automated test suites, post-processing scripts, and a documentation website.
Key Features
- ALE Formulation Integration: Native ALE support integrated into the SPS solver to handle moving and adaptive meshes.
- Conservative Interface Methods: Conservative level-set and ghost-fluid techniques adapted to remapping and mesh adaptation.
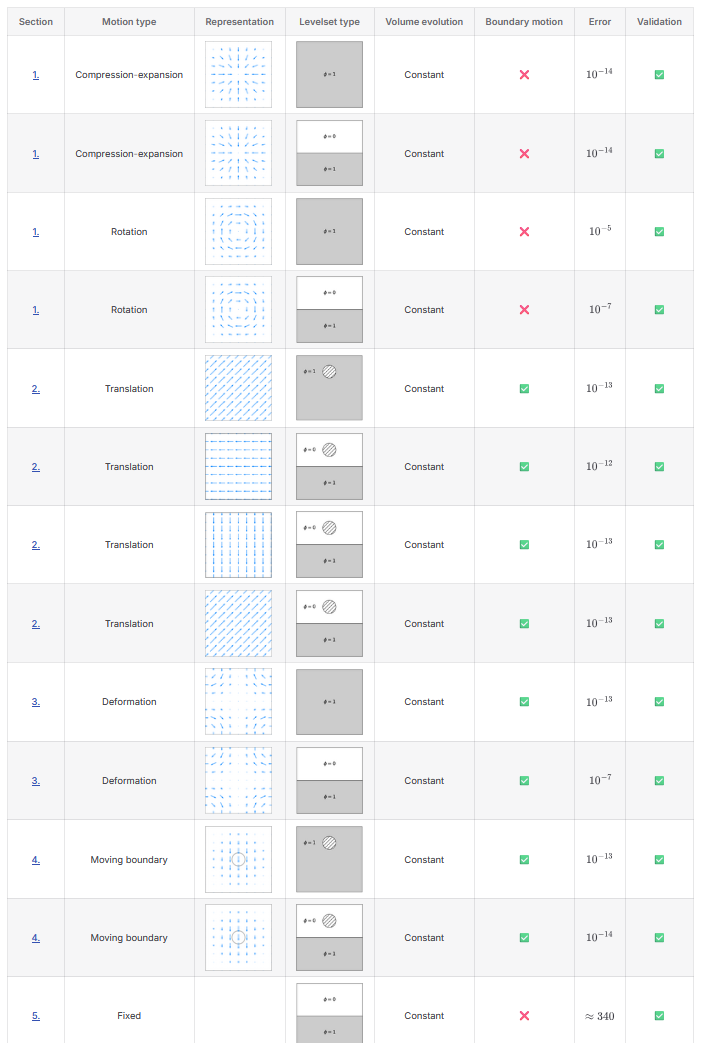
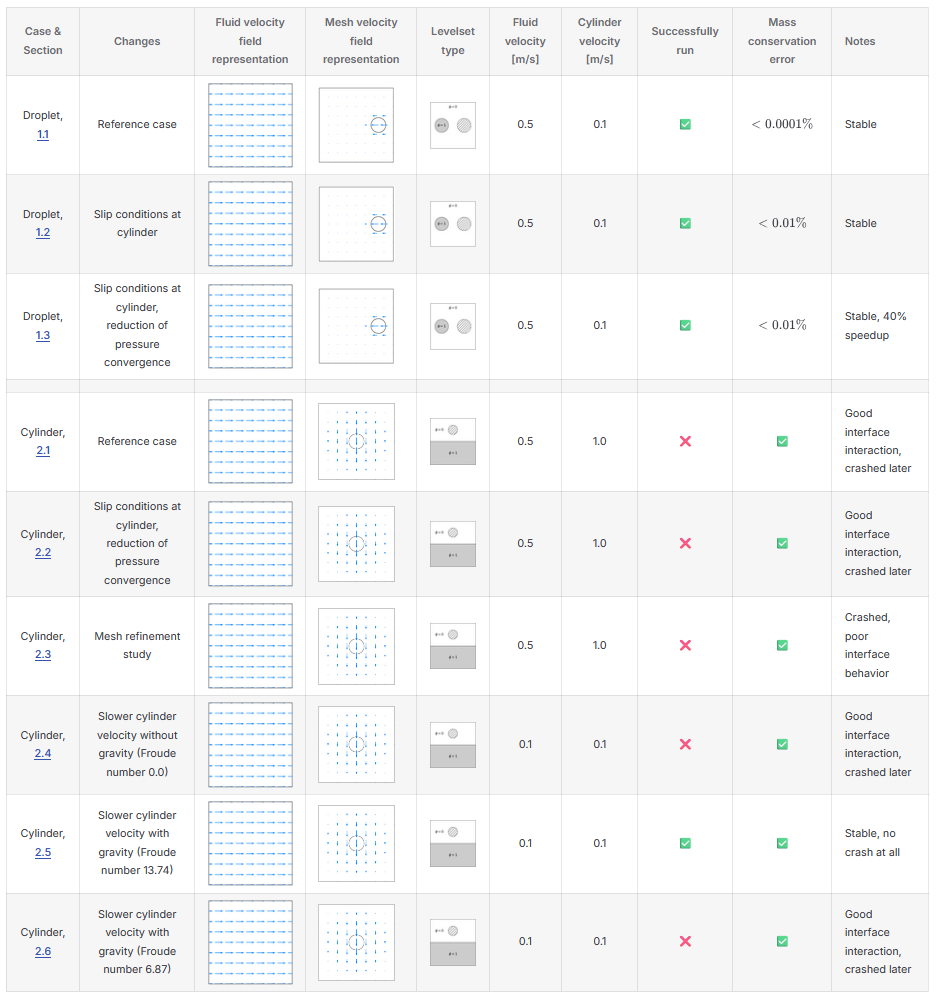
- Validation & Test Suite: Unit and integration tests on canonical two-phase cases (droplet dynamics, falling cylinder) to assess conservation and robustness.
- Automation & Post-processing: Python scripts for run automation, ParaView frame extraction, and video assembly with FFmpeg.
Challenges and Learnings
- Conservative ALE Implementation: Stepwise development from a basic incompressible solver to a full ALE-capable two-phase solver, ensuring discrete conservation (mass, momentum) under mesh motion.
- HPC Limitations: Limited local resources required use of the CRIANN supercomputer for high-resolution validation runs.
- Robustness with Mesh Adaptation: Addressed numerical issues arising from dynamic mesh adaptation and interface reconstruction; identified follow-up tasks to harden interpolation/remapping routines.
Showcase
Project Organization
To ensure the success of the internship, a strict organization and documentation workflow was put in place. A dedicated website was used to track progress. Main elements:
- Weekly Reports: Short weekly summaries covering progress, blockers, and next steps.
- Meeting Minutes: Documentation of participants, topics, and decisions for traceability.
- Resource Sharing: Centralized repository for videos, figures, animations, and code to avoid size/version issues.
- Facilitated Supervision: The website enabled supervisors to follow progress efficiently.
This structure helped the team remain focused while maintaining clear communication.
| Weekly Report | Research Progress |
|---|---|
 |  |
Example Test Cases and Validation
| Levelset Solver | Spray Solver |
|---|---|
 |  |
Final Results
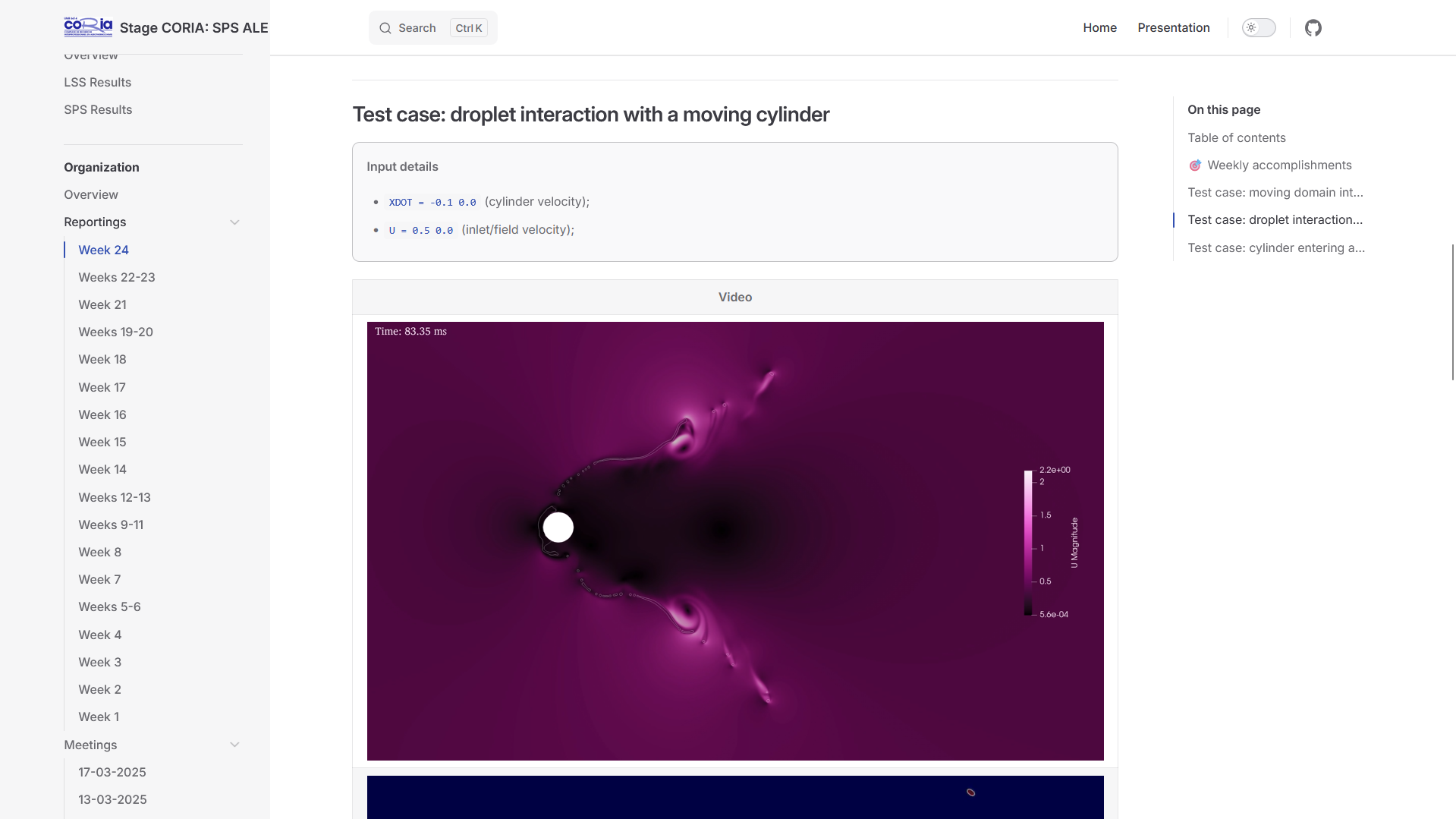
Validation comparisons and selected results (example): droplet dynamics and falling cylinder cases showcasing interface evolution and velocity fields.
DROPLET Test Case: velocity and liquid-gas interface |
|---|
FALLING CYLINDER Test Case: velocity field and liquid-gas interface |
|---|
Conclusion
This internship delivered a compact, maintainable ALE implementation for the SPS solver in YALES2, validated on canonical two-phase cases and compatible with dynamic mesh adaptation. The solver shows good conservation properties (including respect of the GCL) and handles mesh motion and complex interfaces, while some limitations remain for strong interface–obstacle interactions. Delivered artifacts (integrated code, test suites and documentation) form a solid base for further work.
Future work (short): improve robustness under large deformations, extend to 3D, and consider hybrid interface methods (e.g. CLSVOF) for stricter conservation.
Personal note
Working at CORIA was highly rewarding. I strengthened my numerical-simulation and software skills, and the internship confirmed my interest in pursuing CFD research or R&D.
Technologies Used
Computational Tools & Services
| Technology | Badge | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| YALES2 (SPS / LSS) |  | Two-phase solvers, ALE implementation, adaptive meshing |
| PETSc / Hypre |  | Linear solvers and preconditioners for Poisson problems |
| CRIANN Supercomputer | High-performance computing resources for simulation campaigns | |
| ParaView |  | Post-processing and visualization of simulation results |
| Python |  | Scripting, automation and data processing |
Documentation
Web Development
| Technology | Badge | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Vue.js |  | Framework used for creating the interactive documentation |
| VitePress |  | Static site generation for the documentation |
| HTML5 |  | Structure of the website |
| CSS3 |  | Design and layout of the website |
| JavaScript |  | Core logic of interactive parts |
| Markdown |  | Writing documentation content |
| LaTeX |  | Typesetting for the technical report |
Backend
| Name | Badge | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| LAMP Stack |  | Full-stack hosting for documentation when required |
| Apache2 |  | Web server for hosting static/dynamic content |
Hosting & Version Control
| Name | Badge | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| OVH |  | Hosting provider for web services |
| Cloudflare |  | CDN and site protection |
| GitHub |  | Version control and CI/CD |
Reporting
| Technology | Badge | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| LaTeX |  | Typesetting system for equations and the technical report |
| Overleaf |  | Collaborative LaTeX editing and report preparation |